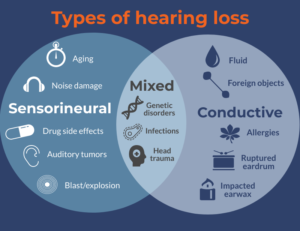
Conductive Hearing Loss
 Video
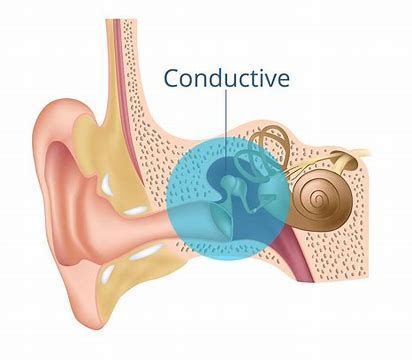
VideoConductive hearing loss – Hearing loss is caused by problem in the outer or middle ear.
Most often the hearing loss is treated medically or surgically.
Examples of some conditions that cause conductive hearing loss are middle ear infections, otosclerosis, perforation of the eardrum.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Video
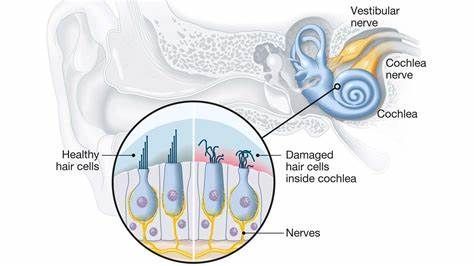
VideoSensorineural hearing loss – Hearing loss is caused by problem in the inner ear or hearing nerve.
Examples of some conditions that cause sensorineural hearing loss are ototoxicity, noise induced hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent. It is managed with hearing aids, cochlear implants or assistive listening devices
Mixed Hearing Loss
 Video
VideoMixed hearing loss – Hearing loss is due to a combination of problems in the outer/middle ear and inner ear. It is managed depending on the nature of conductive loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
Central Hearing Loss
Hearing loss caused due to dysfunction in the central auditory processing system, which includes the auditory nerve and the brain's auditory pathways.
This condition can result from various causes, such as neurological disorders, brain injury, or degenerative diseases, and affects the individual's ability to interpret and understand sounds.
